Organic Rankine CycleORC PROCESS by TurbodenTHE RANKINE CYCLE The Rankine Cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that converts heat into work. The heat is supplied to a closed loop, which typically uses water as working fluid. The Rankine Cycle based on water provides approximately 85% of worldwide electricity production. The Organic Rankine Cycle's principle is based on a turbogenerator working as a conventional steam turbine to transform thermal energy into mechanical energy and finally into electric energy through an electrical generator. Instead of generating steam from water, the ORC system vaporizes an organic fluid, characterized by a molecular mass higher than that of water, which leads to a slower rotation of the turbine, lower pressures and no erosion of the metal parts and blades. |
 |
|
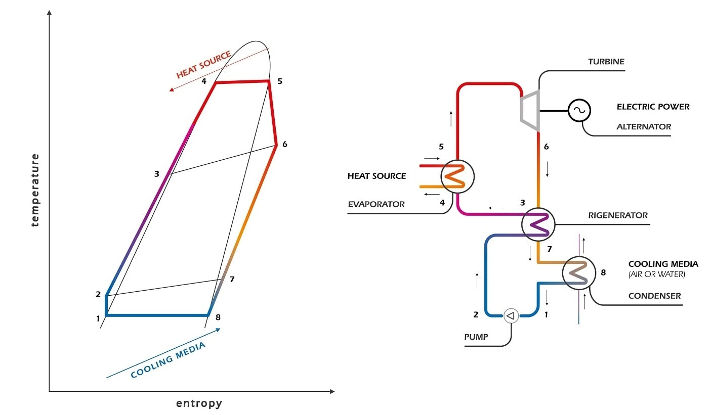
The ORC turbogenerator uses medium-to-high-temperature thermal oil to preheat and vaporize a suitable organic working fluid in the evaporator (4>5). The organic fluid vapor rotates the turbine (5>6), which is directly coupled to the electric generator, resulting in clean, reliable electric power. The exhaust vapor flows through the regenerator (6>7), where it heats the organic liquid (2>3) and is then condensed in the condenser and cooled by the cooling circuit (7>8>1). The organic working fluid is then pumped (1>2) into the regenerator and evaporator, thus completing the closed-cycle operation. |
|
APPLICATIONS |
|
Biomass
Turboden ORC plants produce heat and electricity from different kinds of biomass with high efficiency and user friendly operation. The generated power ranges up to 20 MW electric per single shaft. 315 plants* *38 plants are under construction |
|
Geothermal 
The ORC technology is particularly suitable for the exploitation of medium-to-low enthalpy sources. It is a cost-effective solution with power outputs reaching up to 40 MWe per single generator for sources with water temperature of 100°C to 200°C or higher. 14 plants* *2 plants are under construction |
|
Waste Heat Recovery 
Turboden ORC units can produce electricity by recovering heat from industrial processes and in combined cycles with reciprocating engines and gas turbines. The power of Turboden turbo generators in this application generally ranges up to 20 MW electric per single shaft. 34 plants* *5 plants are under construction |
|
Oil & Gas 
Turboden ORC units enable power production by recovering excess waste heat from the exhausts of gas turbines or reciprocating engines, or from the hot streams typical in Oil & Gas industry. ORC turbogenerators provide a solution to improving the efficiency of typical Oil & Gas processes, by allowing users to reduce their environmental footprint through converting waste, high-to-low grade heat, into mechanical/electric power. 4 plants* *2 plants are under construction |
|
Waste to Energy 
Turboden Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) technology can be profitably and efficiently used to produce electric and thermal power from waste and to enhance the efficiency of existing waste to energy plants. Turboden ORC turbogenerators in this application are able to produce up to 40 MW of electric power per single generator. 19 plants* *8 plants are under construction |
|
Concentrated Solar Power 
Turboden units allow to convert the heat collected by solar collectors into electricity through an efficient thermodynamic cycle. Concentrated Solar Power systems with the ORC technology of Turboden can be cost-effective in the range up to 20 MW electric per single shaft. 5 plants* *2 plants are under construction |
|
Steam & Power 
ST&P®, Turboden Steam & Power ORC system, is a new technical solution for Combined Heat & Power (CHP) generation, with a very high overall energy efficiency, directly employed in manufacturing and industrial processes. It allows the production of electricity and a valuable high temperature heat carrier, such as steam, directly exploitable in manufacturing processes. |